Standards within the pharmaceutical industry are vital for enhancing worldwide health and ensuring the safety of patients. One such standard is the Identification of Medicinal Products (IDMP), designed to enable the reliable global exchange of medicinal product information. This framework is especially relevant to IDMP pharma initiatives, where standardization ensures consistent data across markets.
Read Also: Data Interoperability in Pharma
The EMA (European Medicines Agency) is facilitating the adoption of these standards by establishing a regulatory framework that makes compliance with IDMP mandatory for all EU states. The FDA will soon follow suit. But there’s more to IDMP regulatory compliance; it represents a strategic decision that can enhance patient safety, streamline operations, and improve data management.
Many organizations are now investing in specialized IDMP software to manage structured product data more efficiently and meet evolving regulatory requirements.
In this article, we will dive into the intricacies of IDMP, exploring its components, the significance of IDMP compliance, and its integration with modern healthcare data standards like HL7 FHIR.
What Is IDMP?

IDMP meaning is derived from its full name: Identification of Medicinal Products. Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), is crucial in global pharmacovigilance and medication safety. These standards offer a universal framework for uniquely identifying medicinal products, coupled with detailed descriptions to ensure uniform documentation and terminologies.
Their significance can’t be overstated for efficient information exchange among international regulators, manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors. This is especially relevant as the FDA and other regulatory bodies address challenges in the global supply chain and foreign sourcing of medicinal products.
The identification of medicinal products standards consists of the following:
Medicinal Product Identification (MPID) – ISO 11615: This standard outlines the data elements and structures necessary for the unique identification and exchange of regulated medicinal product information. It includes product names, clinical details, pharmaceutical properties, packaging, marketing authorization, and manufacturing information.
Pharmaceutical Product Identifier (PhPID) – ISO 11616: PhPID focuses on the unique identification of medical products based on pharmaceutical composition. It considers elements like substances, strengths, reference strengths, and dosage forms.
Substance Identification (SubID) – ISO 11238: SubID defines the substances in medicinal products by their primary, general characteristics, aiding in the unique identification and information exchange regarding these substances.
Dosage Form and Route of Administration – ISO 11239: This standard provides data elements and structures for the unique identification of pharmaceutical dosage forms, units of presentation, routes of administration, and packaging.
Units of Measurement (UoM) – ISO 11240: UoM specifies the rules for units of measurement. It establishes requirements for traceability to international metrological standards and provides structures for mapping between different unit vocabularies and language translations.
Why Does IDMP Compliance Matter?

IDMP compliance ensures greater safety, efficiency, and transparency in the global medicinal product lifecycle, from development to patient delivery. It significantly contributes to public health safety by improving drug traceability, regulatory processes, and pharmacovigilance activities. Let’s examine these benefits more closely!
Enhanced Drug Safety and Pharmacovigilance
The global adoption of IDMP standards facilitates the unique identification and uniform exchange of medicinal products and substance identifiers. This uniformity is crucial for improving the accuracy of signal detection in pharmacovigilance. By using common identifiers in Individual Case Safety Reports (ICSRs), regulatory bodies can more efficiently process data and accurately associate adverse events or product quality defects with specific products or substances globally.
With IDMP compliance, adverse events become easier to trace back to specific products. A universal identifier for a drug can be referenced in ICSRs, allowing for faster international identification of potentially dangerous products.
Improved Medicinal Product Traceability in Global Supply Chain
IDMP identifiers provide detailed information on medicinal products, including proprietary names, common names, dose forms, strengths, package sizes, and batch identification. This level of detail enhances supply chain visibility, improving traceability and integrity. It protects patients from substandard or counterfeit products, thereby safeguarding public health.
Consistency Across Product Lifecycle
Previously, a product or active substance might receive different names and terminologies at various stages of its lifecycle. With IDMP standards, there is a move towards standardization and simplification of medicinal data. This uniformity leads to efficiency and faster time-to-market.
Operational Efficiencies for Regulatory Departments
ISO IDMP compliance simplifies the generation and sharing of documentation for regulatory departments. It eases the compliance burden, reduces operational costs, and diminishes inconsistencies in documentation.
Simplified International Product Registration Comparisons
Standardized IDMP-structured data exchange simplifies comparing product registrations across different countries and regions. This standardization is crucial in managing batch-release processes and addressing medicinal product shortages more effectively.
IDMP Compliance in Europe
With the IDMP compliance deadline in Europe having passed in April 2023, the pharmaceutical industry is now navigating a new regulatory landscape. The EMA’s integration of the Digital Application Dataset Integration (DADI) interface has significantly influenced the compliance processes for medicinal product information.
Pharmaceutical companies must adapt to the DADI user interface for structured data submissions. This change, which replaced the electronic Application Form (eAF), has been a significant pivot in the industry’s approach to data management. Companies that have made substantial progress in IDMP implementation or had robust data management frameworks in place have had to ensure their systems and processes comply with the new requirements. This transition has been more challenging for organizations that were less advanced in their preparation, necessitating a rapid alignment with the DADI requirements alongside their ongoing IDMP efforts.
The current focus for companies lies in managing their data effectively under the new framework. This includes adhering to the Substance, Product, Organization, and Referential (SPOR) data specifications and integrating the additional DADI fields. Effective data governance has become more critical than ever, emphasizing data accuracy and consistency across various regulatory submissions.
As the industry moves forward post-deadline, the focus is on compliance and leveraging these new requirements to enhance data quality and operational efficiency. The eventual goal is to achieve full IDMP implementation, which promises a more interconnected and streamlined regulatory environment. The integration of the FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) format in future submissions will further enhance the seamless exchange of medicinal product information between the industry and regulators.
IDMP Compliance in the US
In the United States, the FDA facilitates and advocates using IDMP standards for identifying medicines (excluding investigational medicinal products).
The FDA’s approach to ISO IDMP standards involves ensuring that existing US systems and identifiers for medicinal products align with and support the goals of the international ISO IDMP standards.
In 2013, the FDA established an internal committee to analyze how well FDA standards conform to ISO IDMP standards. This analysis included evaluating the Unique Ingredient Identifier (UNII), Structured Product Labeling (SPL) Pharmaceutical Dosage Form Terminology, Unified Code for Units of Measure (UCUM), and National Drug Code (NDC):
- Unique Ingredient Identifier (UNII): The UNII, conforming to ISO 11238, is an alphanumeric code used to uniquely identify substances in medicinal products. The FDA, in collaboration with the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS/NIH), developed a Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) compatible with ISO 11238. This system allows for consistent identification of substances in line with international standards.
- SPL Pharmaceutical Dosage Form Terminology: For ISO 11239, which focuses on pharmaceutical dosage forms, the FDA uses various terminologies, including the SPL Pharmaceutical Dosage Form Terminology and the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms. The FDA is working with stakeholders to develop a solution for a global Pharmaceutical Product Identifier (PhPID), which requires a central dosage form terminology.
- Unified Code for Units of Measure (UCUM): In compliance with ISO 11240, UCUM is a standard for coding units of measurement, facilitating unambiguous electronic communication in medicinal product characteristics. In 2019, the FDA adopted the latest set of UCUM codes, supporting its use in drug establishment registration, drug listing, and regulatory submissions.
- National Drug Code (NDC): Regarding ISO 11615, the FDA continues to use the NDC as the unique identifier for US medicinal products. The NDC, comprising a labeler code, product code, and package code, aligns well with the ISO 11615 concepts and specifications. Adding the “US” country code to the NDC creates a code comparable to the ISO MPID (Medicinal Product Identification).
The FDA’s approach towards IDMP compliance demonstrates a strong commitment to aligning US standards with international ISO IDMP standards. By evaluating and adapting key components like UNII, SPL, UCUM, and NDC, the FDA ensures that medicinal products in the US are consistently and uniquely identified, facilitating global data exchange and enhancing drug safety.
This alignment streamlines regulatory processes and strengthens the integrity of the global pharmaceutical supply chain, ensuring more effective pharmacovigilance and patient safety.
Leveraging HL7 FHIR for IDMP
FHIR, developed by Health Level Seven International (HL7), is a standard for electronic health data exchange. It uses a modern web-based suite of API technology to enable disparate health systems to communicate effectively. FHIR is designed to be simple to implement and to facilitate the exchange of electronic health records.
FHIR and IDMP are integral to improving the interoperability of healthcare systems in terms of medicinal product information. By incorporating IDMP standards into FHIR resources, healthcare and regulatory systems can uniformly identify and exchange data about medicinal products.
- Efficient Data Exchange: By aligning IDMP standards with FHIR resources, the healthcare industry can more efficiently exchange detailed product information. This includes details about pharmaceutical products, their ingredients, dosages, and packaging.
- Pharmacovigilance and Regulatory Compliance: The integration facilitates better pharmacovigilance practices and regulatory compliance. For example, adverse drug reactions can be more accurately tracked and associated with specific medicinal products.
- Global Product Identification: With FHIR implementing IDMP standards, it becomes easier to identify medicinal products across different healthcare systems and national boundaries. This is especially useful for international regulatory agencies, pharmaceutical companies, and healthcare providers.
IDMP Compliance Solutions and Mapping to the FHIR Format
FHIR, a versatile standard for healthcare data interchange, is well-positioned to align with ISO IDMP standards. This alignment process involves creating resources in FHIR that closely map to the data structures and requirements of IDMP. The aim is to make FHIR a natural fit for IDMP, catering to pharmaceutical companies, regulators, and other stakeholders who require access to detailed medicinal product information.
In FHIR V5, the most current version of the standard, the MedicinalProductDefinition is used to define and detail medicinal products and their properties.
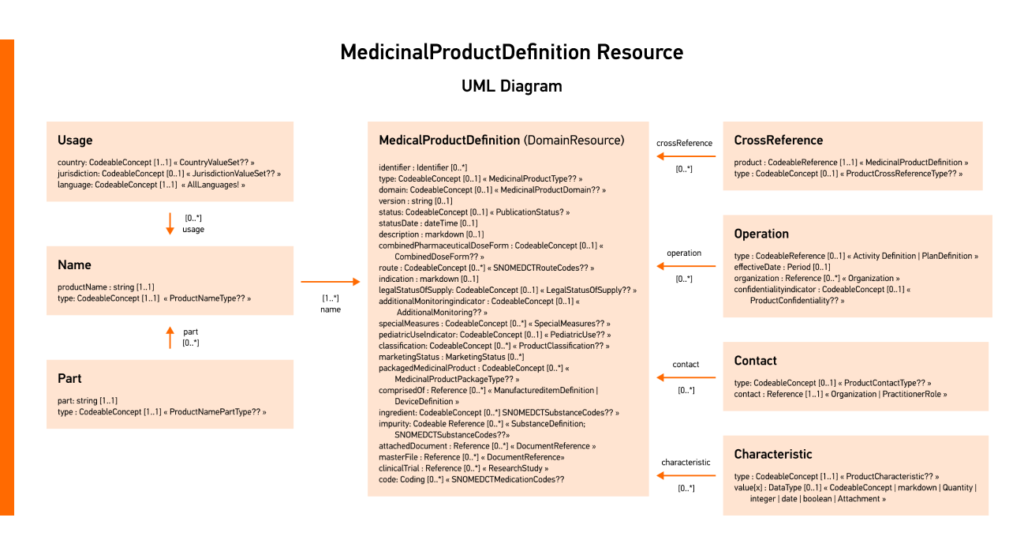
Iperion, a Deloitte business in collaboration with Edenlab, developed an end-to-end IDMP solution that streamlines the conversion of IDMP data into FHIR format. This IDMP compliance solution addresses the complexities of transforming IDMP data and is crucial for regulatory submissions and future advancements like ePI.
- AI-Powered Data Collection: Iperion uses its AI tool, DocQMiner, to collect and remediate IDMP data from various sources. This innovative approach allows for the efficient gathering and processing of complex pharmaceutical data.
- Transformation to FHIR Format: The Kodjin FHIR Server is tailored to transform structured IDMP data into the FHIR format. This process makes the data compatible with modern digital health ecosystems.
- Validation and Transmission: Once transformed, the data undergoes rigorous validation and is prepared for transmission. The server’s advanced capabilities, including RESTful API operations, facilitate this process, ensuring the data is query-ready and compliant with industry standards.
Takeaway
While implementing these complex standards does pose certain challenges, regulatory bodies like the FDA, EMA (European Medicines Agency), and WHO (World Health Organization) are adopting a phased approach, focusing on high-impact areas such as regulatory submissions and device integration.
Globally, IDMP (Identification of Medicinal Products) is poised to significantly advance regulatory collaboration, streamline healthcare processes, and empower data-driven insights for enhanced therapeutic outcomes. The concerted efforts of the FDA, EMA, and WHO in aligning with these global standards underscore their collective leadership in promoting healthcare excellence internationally and advancing global health and patient safety.






