The pharmaceutical industry holds a strong position in healthcare and the global economy, with Statista projecting a pharmaceutical market revenue of $187.20B in 2023. Beyond substantial revenues, the pharmaceutical industry contends numerous challenges, including data interoperability problems that hinder workflow efficiency within the market and healthcare in general.
Like other industries within healthcare, pharma requires a specific approach to data management to support its various needs, such as discovering, developing, manufacturing, and marketing medications to cure diseases and ensure patients’ well-being. To maintain these processes, all components of the pharmaceutical industry must cooperate extensively and support the highest level of pharmaceutical data integrity and interoperability.
Maintaining pharma data integrity means keeping data complete, consistent, and accurate throughout its lifecycle and meeting standards for easy access and security. Data integrity is essential for maintaining regulatory compliance in healthcare; however, without data interoperability in pharma, supporting transparent, secure, and standardized information exchange becomes impossible and complicates patients’ access to medications.
Challenges of Data Interoperability in Pharma Industry
The Health Information Technology Advisory Committee (HITAC) analyzed the state of pharmacy interoperability to inform ONC’s interoperability vision. HITAC’s recent report outlines the challenges of pharmacy data interoperability in the US, lowering efficiency in information exchange for medication management.
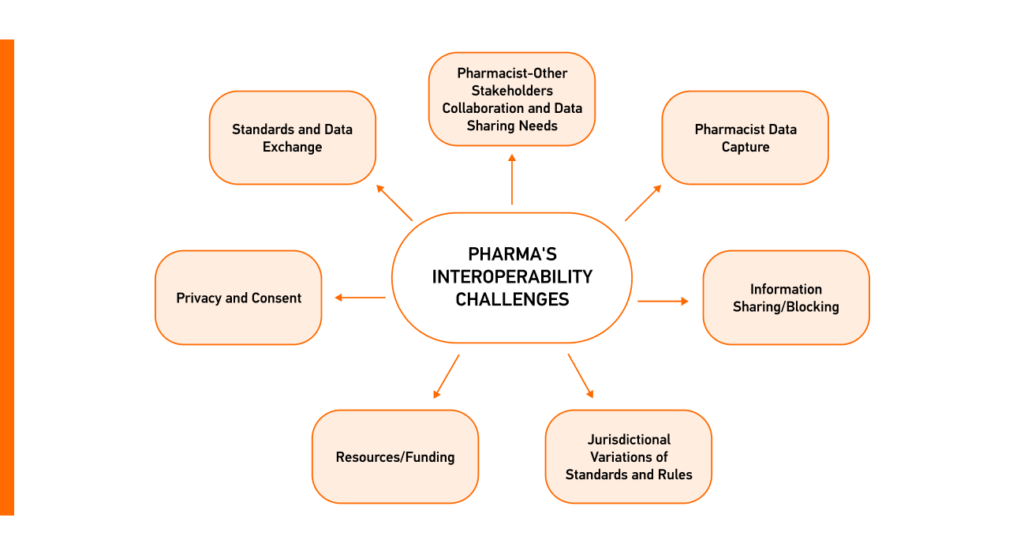
Overcoming these barriers demands concerted efforts, investments, policy alignment, and standardized representation of medicinal products for a more interconnected and efficient use and exchange of interoperable data in pharma.
Medication is heavily regulated and described in detail in the Identification of Medicinal Products (IDMP) standard used worldwide to support the safety of medicinal products. There are challenges to using it that require specific strategies and technologies to ensure all healthcare stakeholders, not just regulatory bodies and pharmaceutical companies, can leverage IDMP effectively.
Exchange of Medicinal Product Information With IDMP: Its Essence and Problems
IDMP is an ISO standard designed to facilitate the precise definition, characterization, and distinctive identification of regulated pharmaceutical products throughout their lifecycle. This spans from the initial stages of clinical development, through the process of obtaining marketing authorization, to the continuous management adjustments and, ultimately, product withdrawal.
The IDMP data model delves into intricate details, from the composition of medicinal products to their manufacturing specifics, packaging details, and regulatory information, and can include hundreds of elements. To effectively manage and exchange this complex data, utilizing a FHIR bundle is essential, as it enables the structured grouping of related resources for seamless interoperability.
Challenges of IDMP
- The IDMP standard is a compilation of distinct standards: IDMP comprises five sub-standards dedicated to capturing and managing medical product data. Such a multi-faceted composition adds complexity, requiring stakeholders to ensure adherence to the requirements set forth by the pharmaceutical regulatory landscape.
- Regulatory requirements: Regulatory agencies globally demand different information for approving and monitoring medicinal products. IDMP aims to meet these requirements with a broad spectrum of data elements and the information required.
- Holistic product description: IDMP goes beyond product names and codes and describes medicinal products, including their composition, manufacturing details, packaging specifications, and regulatory approvals. This extensive coverage caters to various stakeholders in pharma. However, not all stakeholders need all the information since it is mainly required for regulatory purposes.
The IDMP data model delves into intricate details, capturing everything regarding a medicinal product. The EU regulatory agencies have been working on promoting the use of IDMP in the pharmaceutical industry while providing opportunities for other healthcare stakeholders to leverage the IDMP data model by incorporating it with a more flexible healthcare data standard.
FHIR vs. IDMP: The Best Option for Representing and Exchanging Medicinal Data
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is leading the way with the Spore program to gradually implement IDMP and make IDMP compliance mandatory in Europe. They manually entered data for specific rules, setting the stage for more capabilities and moving to electronic data exchange.
An important part of IDMP’s future in Europe is the connection with the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) standard. The EMA is committed to using HL7 FHIR to share electronic data to make different systems in the pharmaceutical sector work together smoothly.
Why Work With FHIR?
- Open source and free standardized healthcare data exchange framework;
- Based on modern technologies (RESTful API, XML, JSON);
- Consists of extensible building blocks (FHIR Resources);
- Increasingly adopted globally (United States, Australia, United Kingdom, Germany, Netherlands, etc.).
The implementation of FHIR for IDMP rolled out in phases, focusing on using FHIR for electronic exchange to change how we handle and share information about medicinal products while ensuring FHIR security protocols are adhered to. Apart from ensuring regulatory compliance in healthcare, particularly the pharmaceutical sector, the standard’s efficiency has already been proven in real-world cases, such as post-market surveillance and electronic product information.
Efficient Post-Market Surveillance (PMS)
The FHIR standard was chosen as the data standard to facilitate information exchange in the EU regulatory network since it allows for re-using product data, ensuring consistency across systems in pharmaceutical regulatory activities, and supporting the data-centric target operating model (TOM).
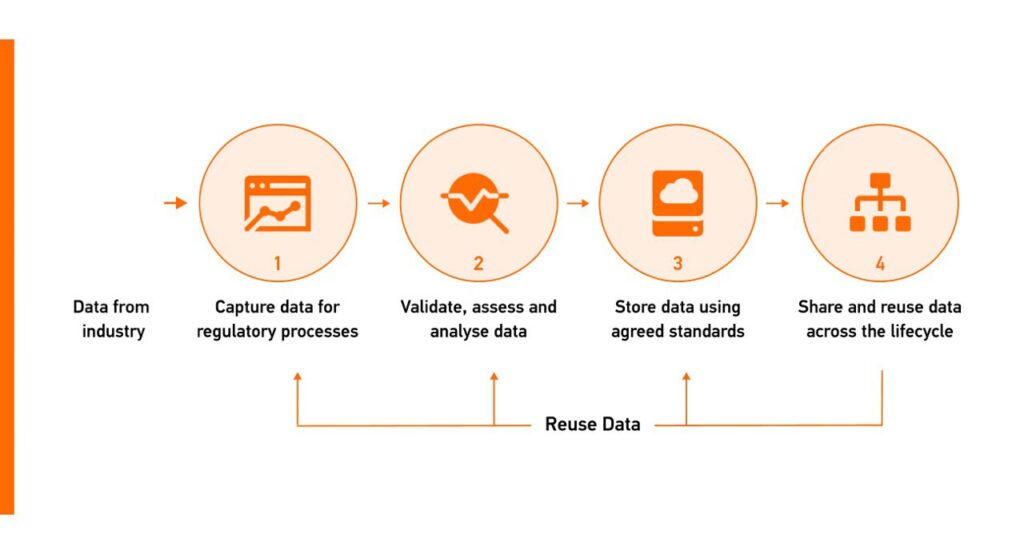
Structuring Electronic Product Information (ePI)
ePI involves two main components: the textual content and the structured data about the product. FHIR’s bundling approach creates a structured composition with headers, sections, images, and a list of products that directs to the organized product data, providing a cohesive way to manage various details in one document.
For example, when dealing with medications of different doses, FHIR ensures a unified presentation, merging written content with structured data to present a complete overview of electronic product information.
Moreover, FHIR supports separating style and content in ePI to distinguish the visual presentation from the actual information and data within the document by providing a standardized framework for structuring and exchanging ePI.
Targeting Challenges of IDMP with HL7 FHIR: Real-World Use Case
Healthcare representatives who don’t need a complex representation of medicinal products can leverage IDMP through FHIR integration. Creating FHIR resources corresponding to the IDMP can simplify the IDMP data model, enabling a more tailored and accessible use of medicinal product information based on specific stakeholder needs and improved pharmacy interoperability.
Thankfully, regulatory agencies in Europe promote the use of IDMP and advocate for its implementation with the FHIR standards, providing opportunities for healthcare stakeholders to leverage the IDMP data model by seamlessly integrating it with the more flexible healthcare data standard without compromising regulatory compliance.
During Edenlab and Deloitte’s webinar, we shared the real-world use case of IDMP and FHIR for enhancing the efficiency of managing medical product information. For the Iperion project, an AI tool was employed to streamline and semi-automate the collection of IDMP data from documents. The Kodjin FHIR Server facilitated transforming the collected data into the FHIR format, along with further data validation.
We highly recommend you watch the webinar on FHIR capabilities for IDMP to gain valuable insights into the dynamic landscape of pharmaceutical industry regulations.

Please contact us with questions regarding the webinar or if you’re aiming for pharma interoperability and adherence to industry regulations. We’ll develop a strategic approach to implement FHIR that optimally aligns with your project’s goals and enhances efficiency.








