Data privacy in healthcare is paramount as it protects sensitive patient information from unauthorized access. In this article, we delve into the importance of data privacy in healthcare and the challenges of protecting sensitive patient data. We will also introduce solutions for overcoming these challenges, such as implementing data protection standards and complying with data privacy regulations.
In our previous article, we shared some huge healthcare data breaches from 2022 and reviewed the unpleasant consequences of such incidents. Hence, healthcare providers must realize the value of healthcare data privacy and prioritize its safety.
So, what is data privacy in healthcare? In this article, we will find out why patient data privacy is important, discuss data privacy challenges, and offer solutions for keeping patients’ data secure and confidential. Healthcare providers can create a safe environment and promote more patient-centered care by understanding the importance of data privacy in the healthcare industry.
What Does Data Privacy Mean in Healthcare?
Why is data privacy important in healthcare?
Data privacy in the healthcare industry refers to protecting sensitive patient data, such as medical history, treatments, insurance data, etc., especially when this data is processed or exchanged via a trusted FHIR vendor solution. Healthcare data privacy is a base for trustworthy relations between patients and healthcare providers since it protects sensitive data from disclosure. One of the major challenges of healthcare data privacy is the protection of EHRs data.
Wide use of EHRs caused the collection and transfer of a large amount of patient data. Unfortunately, not all systems are integrated with a supreme data protection mechanism. Moreover, poor access control via third-party applications also contributes to the list of data privacy issues in healthcare.
Another concern of data privacy in healthcare is compliance with healthcare regulations, which require strict data protection measures, training personnel on the subject of data protection, and following robust security practices.
Human error can also become a cause of healthcare data privacy violations. Accessing data via personal devices and sharing data with unauthorized individuals can cause much harm to both patients and healthcare providers. Hence, every healthcare organization requires basic data protection measures like a robust privacy and confidentiality protection plan, including measures like sensitive data encryption, regular backups, strict data access policies and monitoring, and regular data protection and privacy in healthcare training for personnel.
Implementing a strict security plan and compliance with healthcare data privacy regulations are the best tools for overcoming data privacy challenges in the healthcare industry and protecting sensitive healthcare data.
Sensitive data is personal information stored and used by healthcare providers. It includes medical histories, personal identification info (e.g., name, address, Social security number), laboratory test results, and other data that must remain confidential. Sensitive data disclosure can have severe consequences for healthcare actors.
Unfortunately, the value of sensitive data makes it a tempting target for hackers and cybercriminals. In one of our previous articles on the importance of healthcare data security, we shared the concerning statistics of data breaches and theft of data from electronic health records. Along with other types of sensitive data, EHRs play a crucial role in healthcare.
Types of sensitive healthcare data
Electronic Health Records (EHRs): EHRs are designed to simplify medical processes and ensure fast real-time patient data access. However, EHRs are helpful when implemented with robust mechanisms of sensitive data protection.
An EHR is a source of confidential medical data, such as diagnoses, medical history, test results, treatments, etc. Timely access to this data directly affects patients’ outcomes since it allows for the most effective and careful treatment.
Personal Identifiable Information (PII): this type of data is used to identify an individual. PII consists of various identifiable elements, including name, date of birth, address, email address, phone number, medical identification number, and other personal data.
PII is collected as a part of patients’ medical records—this data allows for tracking patients’ histories and conducting medical research. Breaches of personally identifiable information can result in monetary fines for healthcare providers. Therefore, PII protection measures should include encryption, authentication, and access control to protect the data from disclosure.
Protected Health Information (PHI): created and stored by healthcare providers in rendering healthcare services. PHI includes patients’ health status data, treatment, diagnosis, test results, and other health information.
PII is one of the most crucial healthcare data since it enables physicians to treat patients accurately. Protected health information is highly sensitive data that requires a robust privacy security mechanism.
Research data: collects data from two sources: clinical trials (includes raw data) and databases (such as EHRs). Research data often includes patients’ identities, treatments, and other sensitive information.
Financial information: includes various types of healthcare-related financial data, such as bills, payment records, and insurance coverage. Medical bills include information about diagnoses and treatments. Insurance coverage includes data about who is insured, policy limits, the policy period, and other sensitive information.
This type of data should be carefully protected since it can be used for data theft, fraud, and extortion. Therefore, the financial information data protection plan should include various safeguards (physical, technical, and administrative) to ensure access for authorized individuals only.
Compliance with data protection regulations is the best way for healthcare organizations to protect sensitive data. Regulations include data protection requirements, such as implementing policies and procedures for interactions with data, regular risk assessment, and other security practices to overcome data privacy problems.
Solving Data Privacy Problems
Leveraging healthcare data protection standards is the best way to address data privacy concerns and follow the best practices that guard data against unauthorized access and breaches. There are several health data protection standards that any healthcare provider must be familiar with before developing a healthcare data governance plan.

HIPAA
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) was developed to ensure patients’ data privacy. HIPAA sets standards for protected health information security in the U.S. This standard includes a set of data privacy rules.
- Privacy Rule: establishes national standards for the security of identifiable health data and regulates the use of PHIs. HIPAA compliance implies the implementation of PHI safeguard policies.
- Security Rule: includes requirements for implementing physical, technical, and administrative safeguards to protect the privacy and integrity of PHI. Moreover, HIPAA requires entities to provide patients with PHI access.
- Breach Notification Rule: requires notification to patients and the Department of Health and Human Services whenever a PHI data breach occurs.
HIPAA rules were designed to give patients control over personal health data and promote its confidentiality. Failure to comply with national standards like HIPAA can result in legal consequences and reputational loss.
HITRUST
The HITRUST Common Security Framework (HITRUST CSF) is a certifiable framework for healthcare data protection. HITRUST is a scalable, flexible, and cost-effective framework.
Implementing the HITRUST framework helps protect sensitive data and helps build trust and confidence in the healthcare system for patients. In addition, the HITRUST framework allows for demonstrating compliance with various standards, such as HIPAA and ISO 27001.
ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is an international standard for information security management. This standard includes requirements for managing systems that safeguard sensitive information. Compliance with ISO 27001 ensures continuous monitoring and enhancement of data privacy performance in the European Union.
The ISO 27001 standard provides a set of controls for protecting sensitive healthcare information. Additionally, HITRUST ISO 27001 offers a framework for implementing information protection measures. The standard also supports compliance with GDPR regulations.
GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a data protection standard widely used in the European Union. The standard protects personal data privacy for EU citizens. Compliance with the GDPR is required for all EU organizations that process personal data, including healthcare applications and organizations.
Under the regulation, organizations must obtain patients’ approval to collect personal data and provide them with an option to request access or correction of personal data. Moreover, GDPR allows patients to file complaints in cases of personal data privacy violations. According to GDPR rules, the responsibility for data breaches lies with healthcare collectors.
SOC-2
The System and Organization Controls 2 is a standard developed and used in the United States. It allows for data security control assessment in organizations that collect and process confidential data. The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) developed five risk assessment criteria:
- Security (the system is protected against unauthorized access)
- Availability (the system is available for operations as agreed)
- Processing integrity (a complete, accurate, authorized, and timely system processing)
- Confidentiality (agreement with clients on what data is confidential and how to use and protect it)
- Privacy (guarantee that the organization is handling data by following the privacy principles outlined in the organization’s privacy notice).
SOC-2 provides a framework for conducting effective data security control. Moreover, it addresses sensitive data privacy challenges and protects healthcare data from unauthorized access.
In conclusion, compliance with patient data protection standards is the best way to establish a reputation as a trustworthy healthcare provider and demonstrate that patient privacy is important.
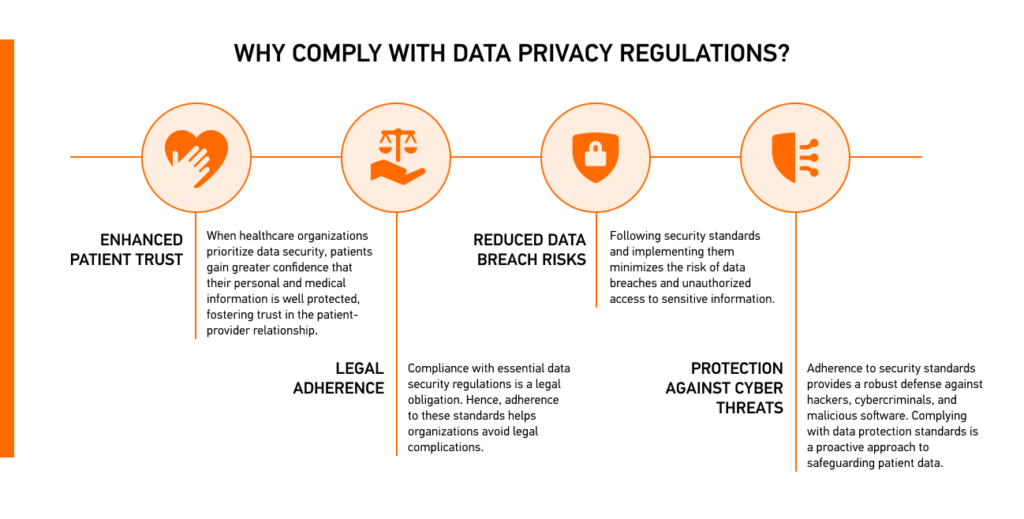
Benefits of Adhering to Standards in Patient Data
Complying with health data privacy and protection standards offers numerous advantages for patients and healthcare providers. These standards are vital for ensuring the integrity, confidentiality, and accessibility of sensitive patient data. Here are the key benefits of such compliance:
Kodjin Will Help You Resolve Data Privacy Issues In Healthcare
A deep analysis of industry needs has allowed our team to create the HIPAA-compliant Kodjin FHIR server. You can see our exceptional domain expertise from the national health system development project. In this project, we implemented an algorithm based on blockchain to protect data in registries from unauthorized changes.
The FHIR server interface will help you reduce the volume of stored and transferred data and enforce a data access control to secure sensitive data from unwanted interactions. Moreover, our server supports all major cloud providers. If you want to know more about what storage solution to choose, read one of our latest articles about healthcare data storage options.
HIPAA compliance of the server ensures sensitive patient data is stored and transmitted in line with healthcare data protection regulations. Our team will help you use an FHIR server to your best advantage and address data privacy problems by providing a secure and client-centered approach to data management.
FAQ
- How do healthcare organizations protect patient information from data breaches?
Healthcare organizations protect patient information by encrypting data to render it unreadable without decryption keys, implementing strict access controls for authorized personnel, continually training staff on data privacy and protection best practices to prevent human error-related breaches, and conducting regular audits to discover vulnerabilities and strengthen security measures.
- What role do healthcare providers and professionals play in data privacy and security?
Healthcare providers and professionals play crucial roles in upholding data privacy and security by ensuring patient understanding and consent for data sharing and use, staying informed about data security practices, promptly reporting security incidents, using strong passwords, etc.
- What are the first steps for a healthcare organization looking to enhance data privacy practices?
To enhance data privacy, healthcare organizations should conduct assessments, ensure compliance, develop policies, train staff, invest in technology, and perform audits, all while complying with healthcare data privacy regulations.






