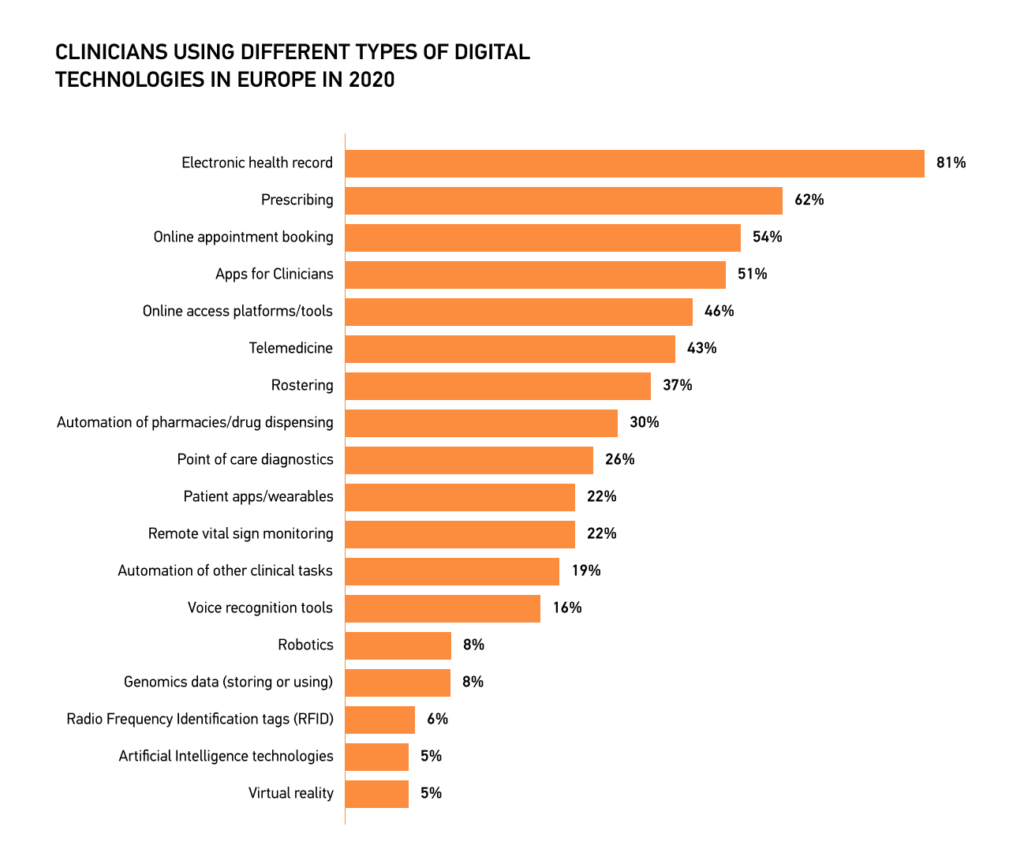
Based on statistics, physicians across Europe have embraced using digital technologies in their practice. For example, 81 percent of European clinicians actively used electronic health records in 2020.
But, behind the exciting opportunities of new technology in healthcare, there’s a big challenge — the need to upskill clinicians for the digital age quickly and effectively. According to a study of healthcare staff digital literacy levels and their attitudes towards information systems, which engaged 407 respondents across a prominent health service, a majority (70-80%) of healthcare staff reported high digital literacy levels and strong confidence in using technology. However, nearly one-fifth of the healthcare professionals expressed anxiety when interacting with information systems.
The lack of confidence when interacting with information systems can lower clinicians’ engagement with digital technologies, ultimately decreasing the quality of care. Hence, ensuring the comfort of healthcare professionals when using digital technologies and empowering them with the necessary digital skills should become one of the industry’s top priorities.
Let’s explore how implementing new technologies — including the need to implement FHIR server as part of interoperable architectures — can help push the right initiatives on a governmental level to help clinicians leverage innovative solutions and improve digital literacy in the healthcare field.
The Challenge: Digital Upskilling for Doctors
Integrating digital systems into healthcare workflows necessitates a fundamental shift in how clinicians approach patient care, data management, and communication, resulting in several challenges that won’t be possible to overcome without clinicians acquiring new digital skills:
- Adapting to New Technologies: The need for using digital health records and telemedicine for data-driven decision-making demands a high level of digital literacy in healthcare and proficiency in new technologies.
- Ensuring Data Accuracy: Accurate and standardized clinical data is the cornerstone of effective treatment. Clinicians must navigate intricate terminologies to code and classify patient information precisely, emphasizing the need for digital upskilling in the medical field.
- Collaborating Effectively: The paradigm shift toward digital healthcare mandates seamless collaboration between clinicians and health information systems. Effective communication allows for exchanging knowledge and improving workflows, highlighting the importance of digital upskilling training.
Terminologies: Empowering Workflows and Communication
Adopting standardized terminologies is key in addressing these challenges and fostering digital literacy for healthcare. These terminologies serve as a lingua franca for clinicians, ensuring uniformity, precision, and efficient data exchange.
ICPC: A Comprehensive Framework for Primary Care
The International Classification of Primary Care (ICPC) is a globally recognized system designed to capture and manage clinical information within primary care settings. Spearheaded and curated by the World Organization of Family Doctors (WONCA) International Classification Committee (WICC), the most recent iteration, ICPC-2, underwent a comprehensive revision in 2015.
The ICPC terminology is formally recognised by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a primary care classification system, which allows for seamless communication between ICPC and the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), enabling synergistic use and collaboration between WONCA and the WHO.
Unique Characteristics of ICPC
- Body System Chapters: ICPC distinguishes itself by organizing clinical information into 17 chapters, each meticulously dedicated to specific body systems or the localization of problems and diseases. This systematic structure simplifies utilization for healthcare providers, ensuring specified and unspecified issues, along with social problems, find comprehensive representation. This inclusivity is paramount for comprehending the dynamics of primary care holistically.
- Episodes of Care (EoC): In contrast to ICD, primarily tailored for single episodes of care within hospital settings, ICPC astutely acknowledges the multi-episode nature of primary care, further emphasizing the need for digital upskilling in the medical field. Healthcare providers frequently grapple with managing multiple episodes of care over time, often dealing with undifferentiated problems. ICPC adeptly captures these episodes, permitting the documentation of the first and last contacts concerning specific health issues. This approach augments the continuity and coordination of care while providing invaluable insights into the evolution of conditions and their associated costs.
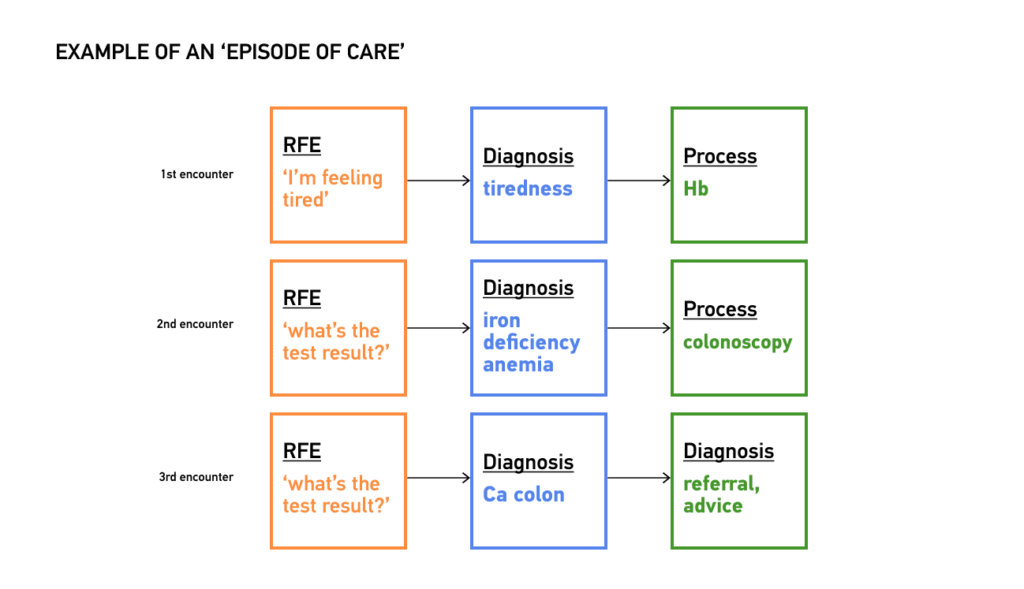
- Reason for Encounter (RFE): ICPC introduced a pioneering concept that sets it apart from ICD — the “Reason for Encounter” (RFE). At the commencement of each patient encounter, ICPC empowers healthcare providers to document the patient’s symptoms and complaints as the RFE, facilitating digital upskilling in the healthcare field. This innovation ensures a seamless linkage of codes from the initial encounter to its conclusion, fostering a more holistic perspective of the patient’s healthcare journey.
ICD: The Universal Language of Diseases
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) serves as the global lingua franca for classifying diseases and health conditions, underscoring the importance of digital literacy for healthcare. Under the World Health Organization’s (WHO) guardianship, the ICD plays a central role in disease monitoring, epidemiology, and billing. While ICD excels in its precision for diseases, it is predominantly tailored for hospital care settings and mortality statistics, rendering it less ideal for the nuanced demands of primary care, highlighting the need for digital upskilling in healthcare.
Empowering Clinicians Through ICPC-2 in Ukraine
Ukraine’s healthcare landscape faced numerous challenges, including outdated healthcare IT infrastructure, clinical registries, and limited computer literacy among clinicians. Edenlab took on a bold mission to modernize the national eHealth system, with ICPC-2 as its central focus, empowering healthcare professionals to enhance their digital skills.
- Modernizing Infrastructure: Ukraine’s healthcare structure yearned for modernization. Edenlab’s team created a Central Component and Open API for the country’s eHealth system, fostering the interconnection of all Health Information Systems (HIS) for the best convenience of Primary Healthcare specialists.
- Simplified Terminology: The stumbling block of outdated clinical registries was circumvented by implementing the ICPC-2 terminology instead of the intricate ICD-10 system, preferred for primary care due to its alignment with typical healthcare cases. The implementation of the ICPC-2 enabled efficient categorization of diagnoses and actions.
- Upskilling Healthcare Professionals: Confronting the stark reality of low computer literacy among General Practitioners (GPs) and the inadequacy of ICT infrastructure, extensive training programs were initiated by HIS’s providers, promoting upskilling for clinicians to ensure a seamless transition into the new system.
- Enhancing Data Management: Creating a Patient’s Cabinet and a Care Plan streamlined healthcare administration, endowed clinicians with a robust framework for securing sensitive patient data, and underscored the importance of digital upskilling for healthcare.
- Optimizing Financial Models: The eHealth project orchestrated a paradigm shift in the financial model. The introduction of e-prescriptions and a fully anonymous monitoring system ushered in a new era of healthcare delivery, concurrently optimizing costs.
Ukraine’s eHealth System: Creating an Online Medical Space for Patients and Pushing the Culture of Digital Literacy Among Clinicians
Overview of eHealth Implementation Results
The development of the Central Component/Open API, expansion into Secondary Healthcare, and the realization of fully anonymous monitoring culminated in the following results:
- Over 36,5 million patient records have been digitized.
- Integration of 14,500 pharmacies has been achieved.
- A network of 6,500 healthcare facilities has been connected.
- Integration of 33 Regional Electronic Health Records (EHRs) has been executed.
- The system efficiently handles 1,000 transactions per second (TPS) under the current system load.
- An astonishing 60 million digital prescriptions have been issued.
Ukraine’s healthcare system is undergoing a digital transformation, with various technologies contributing to its progress, showcasing how the right technology can revolutionize healthcare practices.
This transformation promises a brighter and more efficient future, benefiting patients and healthcare providers, facilitating healthy competition between providers of HIS, and encouraging them to create solutions with comprehensive UI and run workshops to improve the skills of clinicians.

How Many Clinicians Went Digital Due to the eHealth System Implementation?
A government mandate required all medical facilities, not just those under the National Health Service of Ukraine (NHSU), to register in the national eHealth system by March 31, 2023. This move aims to standardize processes, streamline health data exchange, and automate workflows for healthcare professionals.
As a result, the national eHealth system experienced a 48% increase in registrations in 2022, with 2,474 institutions joining. This led to a significant rise in registered healthcare professionals, from over 288,000 in January 2022 to nearly 320,000 in December 2022.
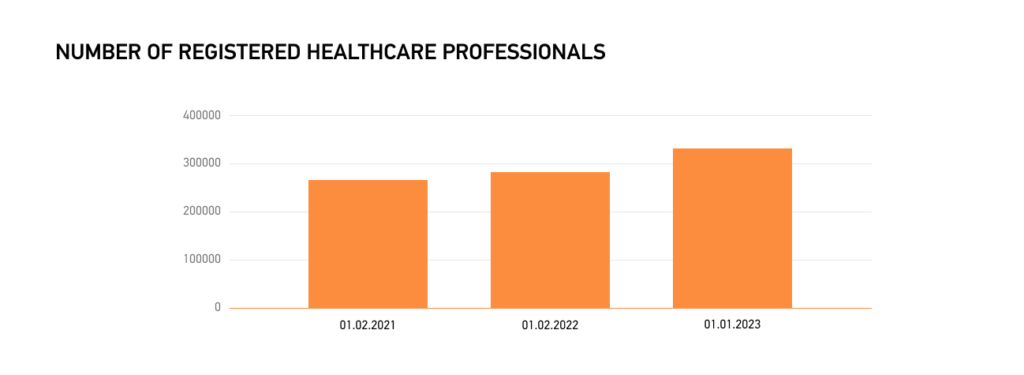
Mandatory registration for NHSU-contracted healthcare providers resulted in 13.9%, which is expected to continue until 100% registration. Integration with other registries ensures real-time updates, underlining the importance of digital literacy for healthcare professionals in Ukraine’s journey toward a fully digitized healthcare ecosystem.
How Does the eHealth System’s Implementation Help With Cultivating a Culture of Digital Literacy Among Ukraine’s Clinicians?
The Ministry of Digital Transformation, in tandem with the Ministry of Health and other partners, developed the “Digital Literacy for Medics” initiative as a proactive measure to address the need for upskilling clinicians and simplifying interactions between patients and healthcare professionals through digitization.
The initiative involves a national test on digital proficiency, which allows healthcare workers to assess their digital literacy levels and identify areas for improvement. The program for upskilling clinicians in Ukraine includes educational materials designed to fill in gaps in digital knowledge and pass the national test on digital literacy. Completing the text rewards healthcare professionals with an electronic certificate that proves enhanced digital savviness and becomes a valuable addition to their portfolio on the top national employment websites.
Final Thoughts
Digital literacy is crucial for effective healthcare delivery, enhanced daily workflows, and streamlined communication between patients and healthcare professionals. The use case of Ukraine’s eHealth system, developed by Edenlab, is an excellent example of how leveraging international health standards can endorse digital technologies in medicine. We invite you to collaborate with us to shape a more digitally proficient and patient-centric healthcare environment.





